Electric Vehicles are growing at a rapid pace across the world. If we trace back to the history of Electric Vehicles, we realize that this technology existed even before the I.C. Engines era. Emission targets set by European union in 2015 during Kyoto protocol are difficult to achieve with existing I.C. Engine vehicles. Hybrid vehicles can reduce CO2 emissions by around 15-20% but that is insufficient in meeting the set targets. Zero emission vehicles concept though not new gained popularity which requires vehicle to be propelled by pure electric means at least for shorter distances. This has propelled resurgence of Electric Vehicles with many companies investing heavily in infrastructure related to it. Availability of high voltage components for vehicle applications has given rise to competition in Automobile domain.
The need to understand architecture related to these components becomes necessary. Following are voltage classes involved:
- Existing 12- or 24-volt architecture for all existing vehicles and accessories
- 48-volt architecture for mild hybrid segment to recuperate energy.
- High voltage architecture for recuperation of energy as well as electric drive.
The need to electrify all existing components in ICE vehicle (e.g., E-steering-Air conditioner, E-suspension etc.) whereas Electric Powertrain requires several hundred volts, the need for standards on high voltage levels becomes prominent every passing day. Existing voltage levels(12/24 volts) will continue in vehicles even in future. The choice of voltage levels depends on applications provided in electric powertrain and will vary with different manufacturers.
Recently 48-volt level is getting popularity in Asia which is used to supply power of more than 3kW for applications such as electric heaters ,electric steering and many such electrical components. Voltages above 60V DC are termed as high voltage in the automobile industry. The advantage of staying below high voltage renders advantage in terms of insulation and contact protection. In automobiles there are only low and high voltages. High voltage lines are orange colored specifying live components and risk associated with handling them. It also acts as visual warning.
Some of the crucial aspects which needs to be in check are as follows:
- Interactions amongst voltage level.
- Different voltage levels should operate independently and simultaneously.
- Standard fuses must be used at each voltage level to ensure protection.
- The occurrence of fault event between two voltage levels should be thought of while designing and additional protection circuits.
- Detection system should be in place.
- Galvanic isolation between different LV levels is required but is extremely important between HV and LV system.
Safety standards related to charging station installations have not evolved specifically for the electric mobility sector and need immediate attention. Potential risk associated with HV are Accidental arcs, electric shocks, EMI/EMC interference and so on. Human body is prone to physiological, thermal, and chemical effects due to electrical shocks. It results in muscle spasms, ventricular fibrillation, and cardiac arrests.
Similarly, companies which were currently dealing with 12, 24 and 48 Volts must also adapt to safety requirements to meet HV conditions. Skilled technicians working in HV domain are key to future service industries. Workplace risk assessment should be conducted for all HV areas such as workshops, laboratories etc. Working and operating procedures need to be developed based on risk assessment to ensure compliance with safety norms. Special marking for HV areas, access restrictions and training to employees are also the need of the hour. Protection measures against direct and indirect contact based on ISO-6469-3 must be implemented.
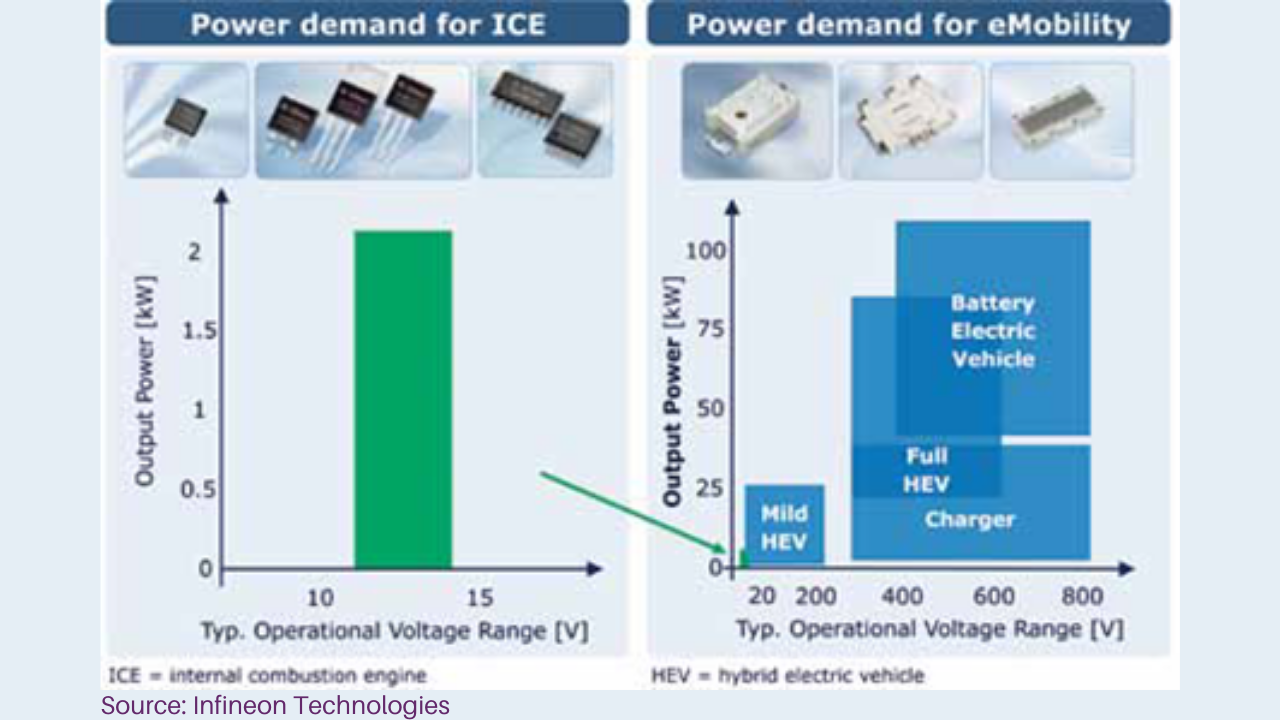
The figure demonstrated above shows the comparison of power demand for ICE and electric vehicles.
Integration of existing technologies safely and reliably into automobiles is an evolutionary process which will require time and shall help in standardization of components and ultimately reduce its cost. Automotive environment will have to adapt to this new developments and manufacturing, operation, and service conditions. A Lot of work is needed in terms of dealing with HV components. Thus, knowledge of Voltage classes is imperative to all stakeholders in E-mobility domain.
To stay abreast with the knowledge of electric vehicles and its various components, one may like to upskill themselves through the following domain of knowledge:
- Electric Vehicle Certification Course (Fundamental)
- Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics
- Basic of Electrical in Electric Vehicle
Happy Learning!
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.

















